Nutritional supplements are available in varying dosage forms like softgels, capsules, and tablets. Each of these forms has its characteristics along with advantages and disadvantages.
The distinction between these forms is pivotal for the supplement and pharmaceutical industries. It affects efficacy and consumer experience. To learn how softgels and other dosage forms are shaping the supplement industry, read Pills, Powders, and Purpose: The Changing Face of Supplements.
Here, we’ll dig into each of these supplement forms in-depth. We’ll also shed light on their vital differences via a comprehensive table.
We’ll also reply to your often-asked inquiries at the end about these forms.
Softgels vs. Tablets vs. Capsules
The following table outlines the pivotal differences between softgels, tablets, and hard-shelled capsules.
| Aspect | Softgels | Tablets | Capsules |
| Dosage | Fixed dosage, typically small | Precise dosage, alterable | Varies (relying on the ingredients) |
| Shape | Soft, hermetic, comprising oil or liquid formulation | Solid, compressed from granules or powder | Two parts (body and cap) generally comprising powder or granules |
| Absorption | It provides easy swallowing with enhanced absorption | Longer absorption than capsules | Generally better absorption
|
| Cost | Generally involves higher costs | Cost-effective and cheaper | Costlier than tablets |
| Production process | Complex production process | Simple and cheaper production | More complex production process than tablets |
| Ingredients | Comprises gelatin, rendering them unfit for vegan and vegetarian diets | Often comprise binders (substances holding the tablet together) | It may comprise gelatin or HPMC (depending on the type) |
| Application and suitability | It is ideal for extracts requiring faster absorption | Suitable for specific, economical doses and portability in consumption | Fitting for varied active ingredients, flexibility, and easiness in usage |
Next, we’ll examine these popular supplement/medication forms in greater detail.
Softgels
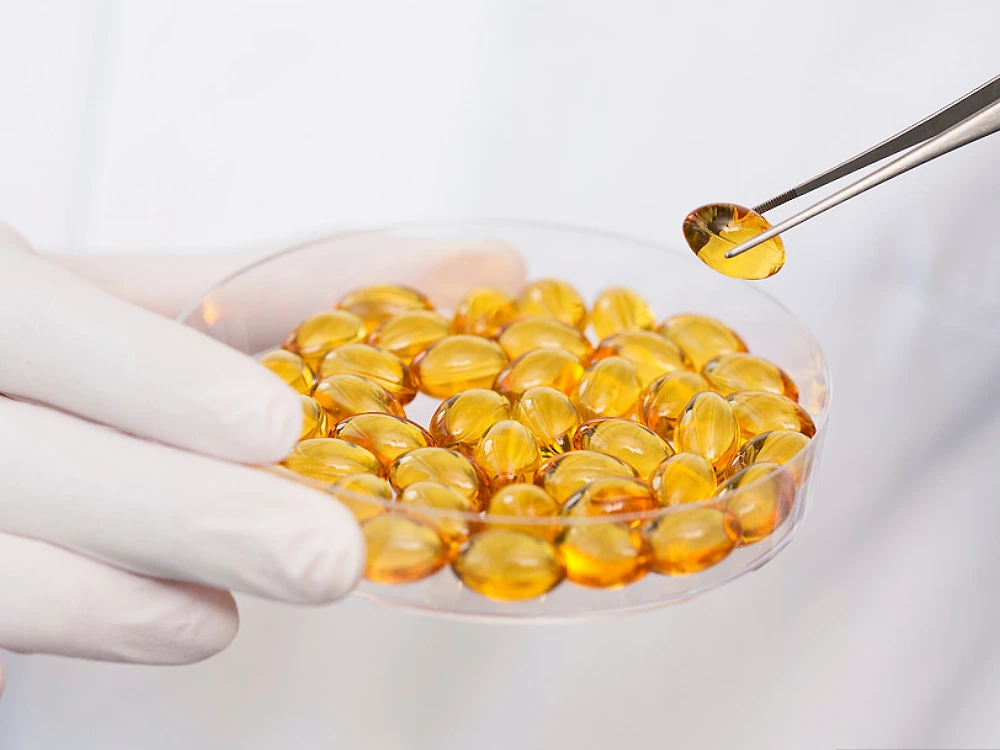

Softgels are a pill variant with ingredients airtightly closed in a softer outer shell. They are a variant of orally ingestible capsules.
Softgels are typically fabricated from animal-derived or vegetarian gelatin and antioxidants. They’re more like a soft outer shell rather than a rigid container.
Such forms are the only practical capsule kind if your formulation is aqueous. Meanwhile, oil-based substances can also be included in hard-shell capsules. Yet, they can’t contain water-based formulations.
Softgel capsules are desirable owing to their ease of swallowing. That’s what consumers generally report when compared to hard-shelled capsules.
They are generally fabricated with one of the following ingredients:
- Gelatin
- Carrageenan
- Tapioca
Pros and Cons of Softgels
The following are the noteworthy pros and cons of such forms:
Pros
- Concealing unpleasant odors and tastes: Softgel capsules can effectively conceal the ingredients’ odor and taste. That makes them pleasant to consume, especially for sensitive patients.
- Improved swallowing: The oval and smooth shape of softgel capsules allows for improved and easy swallowing.
- Better absorption and bioavailability: The softgels’ semi-solid or liquid content provides better absorption and bioavailability of the active ingredient. That’s because dissolution is swifter than that of solid dosing forms.
- Tamper-resistant: They are typically more tamper-resistant than tablets and capsules. It’s because they are closed airtightly.
Cons
- Immediate-release dosing form: Softgels are typically immediate-release dosing forms. That implies they aren’t ideal for supplements necessitating a delayed or sustained release profile.
- Animal-derived gelatin: They are principally fabricated via animal-derived gelatin. That makes them vegan- and vegetarian-unfriendly. They are also unsuitable for individuals with cultural or religious dietary constraints.
- Incompatible with powdered ingredients: They are furthermore incompatible with powdered ingredients.
Capsules
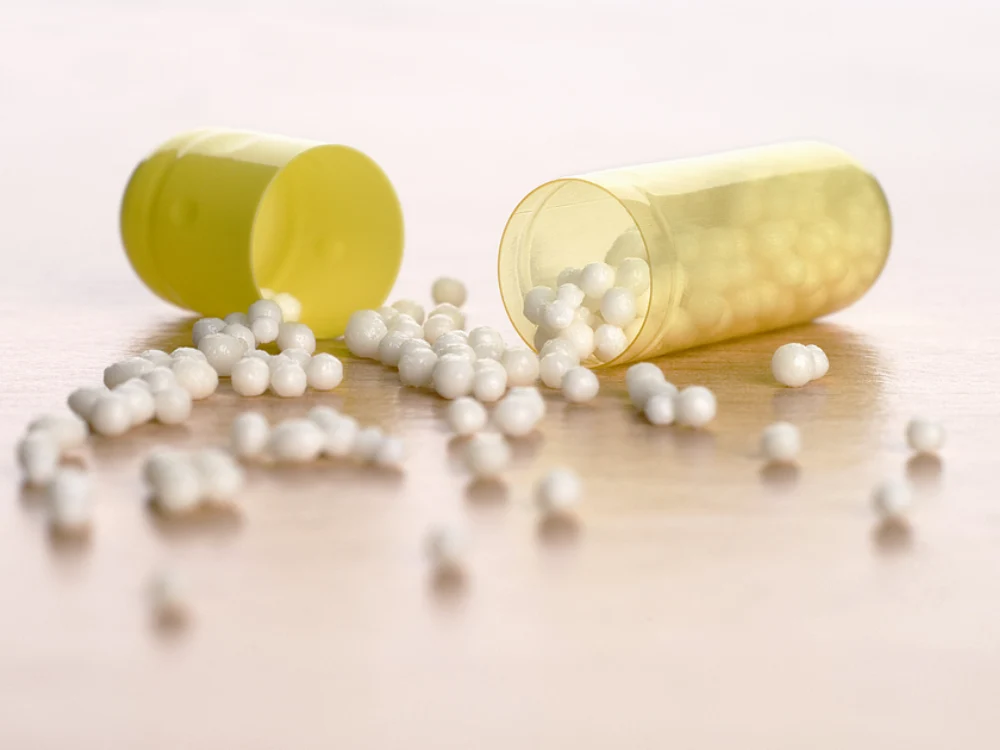
Capsules employed in the supplement industry comprise a hard shell. It’s typically made from gelatin, incorporating an oil-based or powdered formulation.
You can see that they incorporate two interlocking halves. One is smaller in diameter than the other to some extent, allowing a flush connection.
Capsules are favorable because of the broader range of substances they can comprise. Sometimes, you can even open them and add their content to drinks or food. Before doing that, check with your doctor. That’s to ascertain this won’t alter the products’ effects.
Yet, for some consumers, their swallowing can be difficult. Supplement capsules are typically made from one of the following three ingredients:
- Gelatin
- Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC)
- Pullulan
Pros and Cons of Capsules
The following are the pros and cons of hard capsules:
Pros
- Easy swallowing: Capsules flaunt a rounded, smooth shape. That allows for easy swallowing compared to tablets, enhancing patient compliance.
- Versatile in a broad range of formulas: They can encompass an extensive range of ingredients, from liquids, powders, and granules. That makes them fit for differing formulations and active ingredients.
- You won’t taste the ingredients: Like softgels, you won’t taste the internal ingredients owing to the gelatin.
- Faster absorption: After swallowing, the capsule’s outer layer will dissolve. Likewise, it allows for speedier absorption than tablets.
Cons
- Elevated costs: Fabricating capsules is pricier and more complex than tablets. It brings about elevated expenses for healthcare systems and consumers.
- Susceptible to cracking open or tampering: Such forms are more vulnerable to cracking open or tampering than tablets. The shell can be cracked open in humidity or manually, thus affecting the internal ingredients.
- Limitations in fitting ingredients: You may require more capsules to get the correct dosage compared to a tablet. It’s like taking two capsules rather than one tablet for the same dose. It’s due to constraints on how many ingredients come in a capsule.
- Technological restrictions: Not every formulation is compatible and fits the hard capsule shell.
Tablets
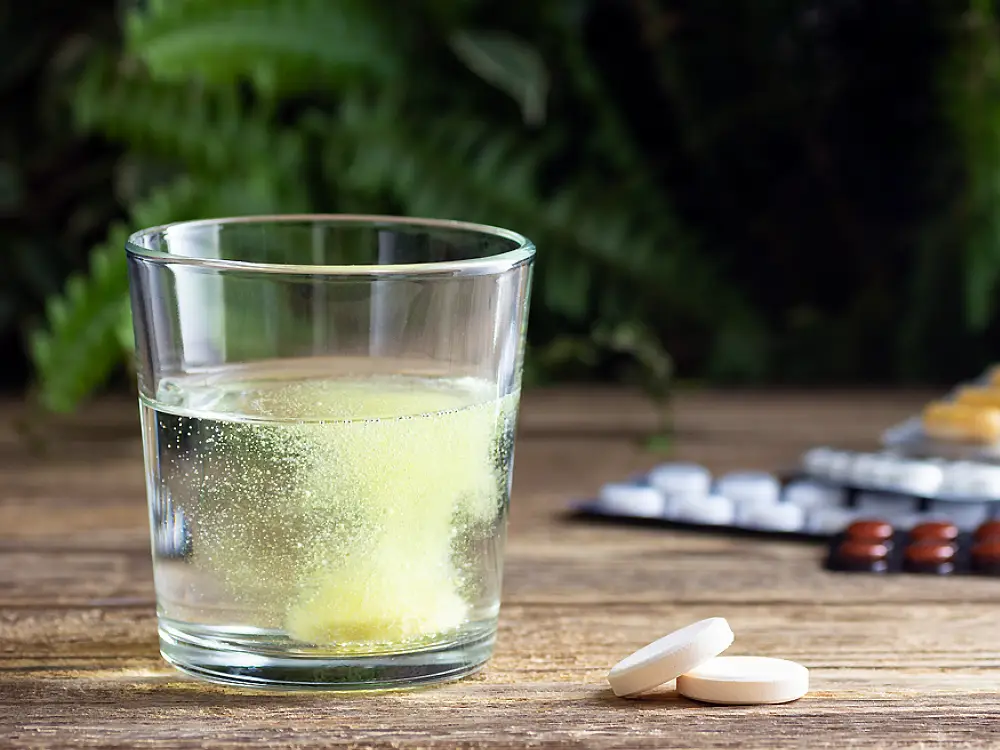

Tablets are compressed, solid forms of supplements and medications. They are fabricated from a powdered version of concentrated constituents.
In other words, they are integrated with a substance that links the powder. The aim is to hold it into a specified shape. Occasionally, such forms are coated, which allows for easy swallowing.
Even though they are primarily made to be swallowed, they can sometimes be chewed. Such chewable tablets typically have flavoring ingredients that make them comfortable to ingest.
Pros and Cons of Tablets
The following are the noteworthy pros and cons of this widely adopted supplement form:
Pros
- Incorporate the highest concentrated dosage: Such forms often comprise the highest concentrated dosage. That implies you can take fewer ones than capsules for the same outcomes. Moreover, they are fabricated with standardized dosing.
- Rapid and cheaper production process: They can be fabricated faster and are more affordable than other forms. That is owing to their straightforward production procedure and cheaper formulas. That makes them cost-effective for healthcare systems and patients.
- Compact sizing: They allow for easy carrying and can be consumed anywhere.
- Variable release forms: Such forms can be fabricated for extended or immediate release of active ingredients. Extended-release ones dissolve into the person’s digestive tract slowly. Meanwhile, immediate-release ones comprise formulas with ingredients that quicken ingestion.
- Some are dissolvable and chewable: Some tablets are dissolvable or chewable. That makes it ideal for those individuals having trouble with swallowing pills.
Cons
- Bitter taste: They typically don’t taste pleasant. The more they sit on your tongue, the worse their taste sounds. As a result, you may experience a bitter flavor in your mouth.
- Hard to swallow: Non-chewable tablets can be hard to swallow, especially for aged people and children.
- Lessened bioavailability: The absorption process of active ingredients in such forms can be lower than that of softgels.
- Possess unsafe ingredients: Such forms may encompass unsafe substances for sensitive people.
FAQs
What Are Softgel Capsules Most Suitable For?
Softgel capsules are suitable for liquid (aqueous) or fat-soluble formulas. That’s owing to the entire encapsulation of the ingredients in gelatin or a similar substance.
Compared to hard capsules, they offer added customization in color and size.
They fit those who experience swallowing issues and need ingredients to be as effectual as possible. They are comfortable to swallow and absorbed faster than other forms like hard capsules.
What Are Tablets More Suitable For?
Tablets are suitable for supplement companies seeking varied doses of a sole formulation. They offer the ability to pack the greatest concentration of ingredients in a single one. With the added capability to split them, they provide the maximal choices for dosages. As a result, people with complicated doses will find them ideal.
Furthermore, they can be fabricated as immediate-release, decayed-release, or extended-release. That augments their versatility.
What Are Capsules More Suitable For?
Hard capsules are more fitting, especially for powdered ingredients. They are a source of higher bioavailability and swifter absorption than tablets.
Besides providing customization and versatility options, they are easier to produce. Individuals with swallowing issues will typically find capsules more comfortable than tablets.
Moreover, in a few cases, capsules can be opened to consume the powder directly, which provides extra flexibility.
Are softgels better than tablets?
The decision to consume softgels or tablets depends on the individual’s circumstances.
Principally, softgels are ideal for liquid extracts requiring swift, easy, and effectual absorption. Some of their examples encompass vitamin D or fish oil. They also allow for comfortable swallowing.
Tablets, in contrast, fit specific dosages and are cost-efficient for solid ingredients. Some examples encompass minerals and vitamin C. Such forms are often more economical than softgels and provide better shelf life.
If the budget concerns you, you may prefer tablets while ascertaining efficacy.
Handian – Leading Supplement Manufacturer

Handian Nutrition is amongst the eminent dietary supplement manufacturers internationally. Established in 1993, we specialize in custom and private-label manufacturing of supplements in differing forms.
Some prominent examples of these include:
Regarding softgels, our admired options include:
We offer varied custom capsule options like:
- Gelatin, vegetarian, halal, and organic
- Varied stock formula types, like maca capsules
- Differing capsule sizes to choose from
About tablets, fabricating high-quality, effervescent, and chewable tablets are our strength.
We possess facilities like multiple automated production lines and cutting-edge machinery for contract supplement manufacturing. Moreover, we have certifications like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and FDA (Food and Drug Administration) certification.
All these showcase our devotion to fabricating high-quality nutritional supplements.
Conclusion
To conclude, softgels, tablets, and capsules have plenty of distinctions. Yet their motive is identical: bring the substances you need to ingest into your body.
Ultimately, it may become a matter of personal preference regarding which form to opt for. It’s a fundamental decision that can influence the efficacy of your daily dietary supplementation.
You can better choose which form suits you, as you are familiar with the distinctions.
